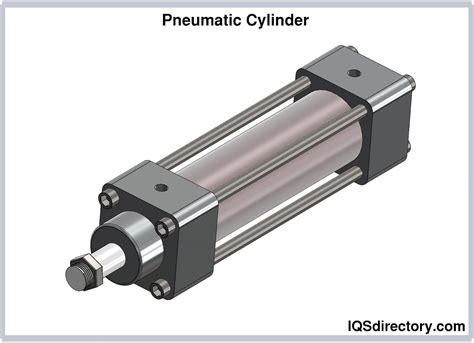
The pneumatic piston cylinder is a fundamental component in pneumatic systems, playing a crucial role in converting compressed air energy into linear motion. This linear motion is then utilized to perform various tasks such as lifting, moving, or pressing objects. The pneumatic piston cylinder's design and functionality are rooted in the principles of pneumatics, which involve the use of compressed air to generate force and motion. In this article, we will delve into the world of pneumatic piston cylinders, exploring their construction, types, applications, and the importance of proper maintenance and selection for optimal performance.
Construction and Operation of Pneumatic Piston Cylinders

A pneumatic piston cylinder typically consists of a cylindrical body, a piston, and a rod. The piston is connected to the rod and moves back and forth within the cylinder, driven by the pressure difference between the two sides of the piston. The movement of the piston is controlled by the introduction and exhaustion of compressed air into and out of the cylinder through ports. The piston’s motion is then transferred to the rod, which extends from the cylinder to perform the desired action. The construction materials for pneumatic piston cylinders can vary, with common choices including steel, aluminum, and stainless steel, each offering different benefits in terms of durability, weight, and resistance to corrosion.
Types of Pneumatic Piston Cylinders
There are several types of pneumatic piston cylinders, each designed to meet specific application requirements. These include single-acting cylinders, where the piston is moved in one direction by compressed air and returns to its original position by a spring or gravity; double-acting cylinders, where the piston is moved in both directions by compressed air; and telescopic cylinders, which provide extended stroke lengths through a series of nested cylinders. The choice of cylinder type depends on the application’s requirements for stroke length, force, and precision of movement. For instance, in applications where space is limited but a long stroke is needed, telescopic cylinders are particularly useful.
| Type of Cylinder | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Single-Acting | Moves piston in one direction with air, returns with spring or gravity | Simple lifting or pushing applications |
| Double-Acting | Moves piston in both directions with air | Applications requiring precise control over both extension and retraction |
| Telescopic | Provides extended stroke lengths through nested cylinders | Applications where space is limited but long stroke is required |

Key Points
- Pneumatic piston cylinders convert compressed air energy into linear motion for tasks like lifting or moving objects.
- The construction of a pneumatic piston cylinder includes a cylindrical body, piston, and rod, with materials chosen for durability and resistance to corrosion.
- Types of pneumatic piston cylinders include single-acting, double-acting, and telescopic, each suited to different application needs.
- Proper selection of a pneumatic piston cylinder involves considering the required force, stroke length, operating conditions, and application environment.
- Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of pneumatic piston cylinders, including checking for air leaks, cleaning, and lubricating moving parts.
Applications of Pneumatic Piston Cylinders
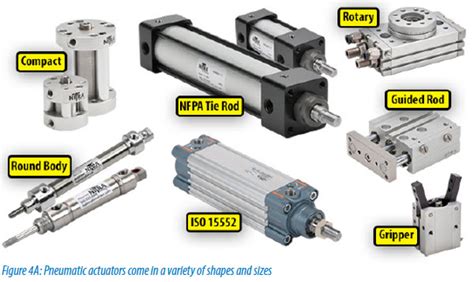
Pneumatic piston cylinders are used in a wide range of applications across various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and medical devices. They are particularly useful in situations where a reliable, consistent, and controlled linear motion is required. For example, in assembly lines, pneumatic cylinders are used to position parts, apply glue, or perform pressing operations. In the medical field, they are used in medical devices and equipment that require precise movement, such as in surgical tools or patient handling equipment.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Maintenance of pneumatic piston cylinders is crucial for ensuring their efficient and reliable operation. Regular checks should be performed to identify any air leaks, which can significantly reduce the cylinder’s performance and increase energy consumption. Cleaning and lubricating the moving parts can also help extend the lifespan of the cylinder. Additionally, the operating conditions, such as temperature and humidity, should be monitored to prevent damage to the cylinder and ensure optimal performance. Troubleshooting common issues, such as erratic movement or failure to extend or retract, often involves checking the air supply, examining the cylinder for physical damage, and ensuring that the control valves are functioning correctly.
What is the primary function of a pneumatic piston cylinder?
+The primary function of a pneumatic piston cylinder is to convert the energy of compressed air into linear motion, which can be used to perform various tasks such as lifting, moving, or pressing objects.
How do I choose the right type of pneumatic piston cylinder for my application?
+Choosing the right type of pneumatic piston cylinder involves considering the required force, stroke length, operating conditions, and application environment. It's also important to consult with a professional or refer to manufacturer guidelines for specific recommendations.
Why is regular maintenance important for pneumatic piston cylinders?
+Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of pneumatic piston cylinders. It involves checking for air leaks, cleaning and lubricating moving parts, and monitoring operating conditions to prevent damage and ensure optimal performance.
In conclusion, pneumatic piston cylinders are versatile and essential components in pneumatic systems, offering a reliable means of converting compressed air energy into linear motion. Their application spans across various industries, and their proper selection, maintenance, and operation are critical for achieving efficient and reliable performance. By understanding the construction, types, and applications of pneumatic piston cylinders, as well as the importance of maintenance and troubleshooting, users can harness their full potential and ensure their systems operate at peak efficiency.