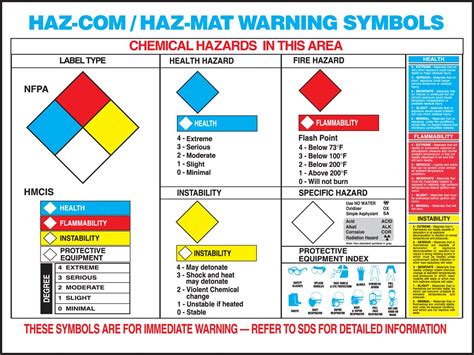
Hazmat labels are a crucial component of the safe transportation and handling of hazardous materials. These labels are designed to provide a clear and concise warning to handlers, transporters, and emergency responders about the potential dangers associated with the materials being shipped or stored. The use of hazmat labels is regulated by various national and international agencies, including the United States Department of Transportation (DOT) and the International Air Transport Association (IATA). In this article, we will delve into the world of hazmat labels, exploring their importance, types, and application guidelines.
Key Points
- Understanding the importance of hazmat labels in ensuring safe transportation and handling of hazardous materials
- Recognizing the different types of hazmat labels, including danger labels, handling labels, and shipping labels
- Familiarity with the application guidelines for hazmat labels, including correct placement, size, and color requirements
- Knowledge of the regulatory agencies governing hazmat labeling, including the DOT and IATA
- Appreciation for the role of hazmat labels in emergency response situations, including providing critical information to first responders
Types of Hazmat Labels

There are several types of hazmat labels, each serving a specific purpose. Danger labels, for example, are used to indicate the level of hazard associated with a particular material. These labels are typically color-coded, with red indicating a high level of danger, yellow indicating a moderate level, and blue indicating a low level. Handling labels, on the other hand, provide instructions for the safe handling of hazardous materials, such as “Do not drop” or “Keep away from heat.” Shipping labels, which include the UN number, proper shipping name, and hazard class, are used to identify the materials being shipped and provide critical information to transporters and emergency responders.
Danger Labels
Danger labels are perhaps the most critical type of hazmat label. These labels are designed to provide a clear and concise warning about the potential dangers associated with a particular material. The DOT has established a system of danger labels, which includes:
| Hazard Class | Description | Label Color |
|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Explosives | Orange |
| 1.2 | Explosives | Orange |
| 2.1 | Flammable gases | Red |
| 2.2 | Non-flammable gases | Green |
| 3 | Flammable liquids | Red |
| 4.1 | Flammable solids | Red |
| 4.2 | Spontaneously combustible | Red |
| 4.3 | Water-reactive | Red |
| 5.1 | Oxidizers | Yellow |
| 5.2 | Organic peroxides | Yellow |
| 6.1 | Toxic | White |
| 6.2 | Infectious substances | White |
| 7 | Radioactive | Magenta |
| 8 | Corrosive | White |
| 9 | Miscellaneous | Green |
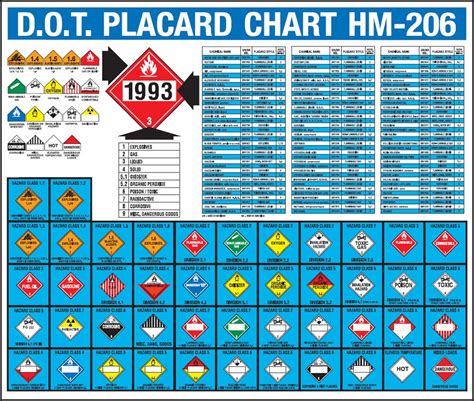
Application Guidelines
The application of hazmat labels is governed by a set of strict guidelines, which include requirements for label size, color, and placement. For example, danger labels must be at least 3.9 inches (10 cm) on each side, with a minimum font size of 1 inch (2.5 cm). The labels must also be placed in a location where they are easily visible, such as on the outside of a shipping container or on the side of a transport vehicle. It is essential to follow these guidelines carefully, as incorrect or incomplete labeling can have serious consequences, including fines, penalties, and even loss of life.
Regulatory Agencies

The use of hazmat labels is regulated by various national and international agencies, including the DOT and IATA. These agencies have established a set of guidelines and regulations for the safe transportation and handling of hazardous materials, which include requirements for labeling, packaging, and documentation. The DOT, for example, has established a comprehensive system of regulations, which includes the Hazardous Materials Regulations (HMR) and the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Regulations (FMCSR). The IATA, on the other hand, has established a set of guidelines and regulations for the safe transportation of hazardous materials by air, which include the IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR).
DOT Regulations
The DOT has established a comprehensive system of regulations for the safe transportation and handling of hazardous materials. The HMR, for example, provides a detailed set of guidelines and regulations for the labeling, packaging, and documentation of hazardous materials. The FMCSR, on the other hand, provides a set of regulations for the safe operation of transport vehicles, including requirements for driver training, vehicle maintenance, and cargo securement.
IATA Regulations
The IATA has established a set of guidelines and regulations for the safe transportation of hazardous materials by air. The DGR, for example, provides a detailed set of guidelines and regulations for the labeling, packaging, and documentation of hazardous materials, as well as requirements for aircraft operations, crew training, and emergency response planning.
What is the purpose of hazmat labels?
+The purpose of hazmat labels is to provide a clear and concise warning about the potential dangers associated with a particular material, as well as to provide critical information to handlers, transporters, and emergency responders.
What are the different types of hazmat labels?
+There are several types of hazmat labels, including danger labels, handling labels, and shipping labels. Each type of label serves a specific purpose and provides critical information to handlers, transporters, and emergency responders.
What are the regulatory agencies governing hazmat labeling?
+The regulatory agencies governing hazmat labeling include the DOT and IATA. These agencies have established a set of guidelines and regulations for the safe transportation and handling of hazardous materials, which include requirements for labeling, packaging, and documentation.
What are the consequences of incorrect or incomplete hazmat labeling?
+The consequences of incorrect or incomplete hazmat labeling can be severe, including fines, penalties, and even loss of life. It is essential to follow the guidelines and regulations for hazmat labeling carefully to ensure the safe handling and transportation of hazardous materials.
How can handlers and transporters ensure compliance with hazmat labeling regulations?
+Handlers and transporters can ensure compliance with hazmat labeling regulations by following the guidelines and regulations established by the DOT and IATA, as well as by providing proper training to employees and using correct labeling and packaging materials.
In conclusion, hazmat labels play a critical role in ensuring the safe transportation and handling of hazardous materials. By understanding the different types of hazmat labels, following the application guidelines, and complying with regulatory agencies, handlers and transporters can prevent accidents, protect people and the environment, and ensure compliance with regulations. As the transportation of hazardous materials continues to evolve, it is essential to stay informed about the latest guidelines and regulations, as well as to prioritize the safe handling and transportation of these materials.