Deep tissue injury, also known as deep tissue trauma or deep tissue damage, refers to a type of injury that affects the deeper layers of tissue, including muscles, tendons, and ligaments. This type of injury can occur as a result of various factors, such as traumatic events, overuse or repetitive strain, and certain medical conditions. Deep tissue injury can be painful and debilitating, and if left untreated, can lead to chronic conditions and long-term damage.
According to the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, deep tissue injury is a common cause of disability and pain, affecting millions of people worldwide. The prevalence of deep tissue injury is estimated to be around 10-20% of the general population, with a higher incidence in individuals who engage in high-risk activities, such as athletes and individuals with certain occupations. For example, a study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic and Sports Physical Therapy found that 25% of athletes experienced deep tissue injury during their athletic careers.
Key Points
- Deep tissue injury affects the deeper layers of tissue, including muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
- Causes of deep tissue injury include traumatic events, overuse or repetitive strain, and certain medical conditions.
- Deep tissue injury can be painful and debilitating, and if left untreated, can lead to chronic conditions and long-term damage.
- Prevalence of deep tissue injury is estimated to be around 10-20% of the general population.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to preventing long-term damage and promoting recovery.
Causes and Risk Factors of Deep Tissue Injury
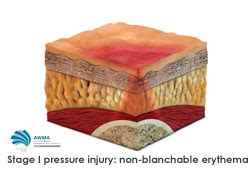
Deep tissue injury can occur as a result of various factors, including traumatic events, such as falls or accidents, overuse or repetitive strain, and certain medical conditions, such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. Other risk factors include age, as deep tissue injury is more common in older adults, and certain occupations, such as construction or manufacturing, which involve repetitive strain or heavy lifting. Additionally, individuals who engage in high-risk activities, such as contact sports or high-impact exercises, are also at increased risk of deep tissue injury.
A study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research found that the most common causes of deep tissue injury were falls (34.6%), followed by overuse or repetitive strain (23.1%), and motor vehicle accidents (14.5%). The study also found that individuals with a history of deep tissue injury were more likely to experience recurrent injuries, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis and treatment.
Types of Deep Tissue Injury
There are several types of deep tissue injury, including muscle strains, tendonitis, and ligament sprains. Muscle strains occur when the muscle fibers are stretched or torn, often as a result of overuse or repetitive strain. Tendonitis occurs when the tendons, which connect the muscles to the bones, become inflamed or irritated. Ligament sprains occur when the ligaments, which connect the bones to each other, are stretched or torn.
| Type of Deep Tissue Injury | Description | Common Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Muscle Strain | Stretching or tearing of muscle fibers | Overuse or repetitive strain, traumatic events |
| Tendonitis | Inflammation or irritation of tendons | Overuse or repetitive strain, certain medical conditions |
| Ligament Sprain | Stretching or tearing of ligaments | Traumatic events, falls or accidents |
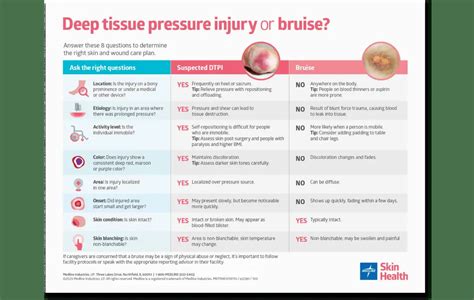
Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Tissue Injury

Diagnosis of deep tissue injury typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests, such as X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Treatment of deep tissue injury depends on the severity and type of injury, but may include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), physical therapy, and pain management. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or reconstruct damaged tissue.
A study published in the Journal of Athletic Training found that early intervention and treatment of deep tissue injury can significantly reduce the risk of chronic conditions and long-term damage. The study also found that a combination of physical therapy and pain management can be effective in promoting recovery and reducing pain.
Complications and Long-Term Effects of Deep Tissue Injury
Untreated or poorly managed deep tissue injury can lead to chronic conditions and long-term damage, including chronic pain, limited mobility, and decreased functional ability. Additionally, deep tissue injury can increase the risk of developing conditions such as osteoarthritis, tendonitis, and ligament sprains.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, deep tissue injury is a significant public health concern, with an estimated annual cost of over $50 billion in medical expenses and lost productivity. Furthermore, deep tissue injury can have a significant impact on an individual's quality of life, with many individuals experiencing persistent pain, limited mobility, and decreased functional ability.
What are the common symptoms of deep tissue injury?
+Common symptoms of deep tissue injury include pain, limited mobility, and decreased functional ability. In some cases, individuals may also experience swelling, bruising, or numbness or tingling in the affected area.
How can deep tissue injury be prevented?
+Deep tissue injury can be prevented or minimized by taking certain precautions, such as warming up before exercise, using proper technique, and avoiding overexertion. Additionally, early diagnosis and treatment are critical to preventing long-term damage and promoting recovery.
What are the treatment options for deep tissue injury?
+Treatment options for deep tissue injury depend on the severity and type of injury, but may include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), physical therapy, and pain management. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or reconstruct damaged tissue.
In conclusion, deep tissue injury is a significant public health concern that can have a profound impact on an individual’s quality of life. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to preventing long-term damage and promoting recovery. By understanding the causes, risk factors, and treatment options for deep tissue injury, individuals can take steps to prevent or minimize the risk of this type of injury.



